What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma refers to a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve and may lead to permanent vision loss (blindness) if untreated. While damage is often associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), it can occur regardless of pressure. If not diagnosed, glaucoma and optic nerve damage usually occur slowly and without pain, silently narrowing the visual field until it is central or fixation vision that is affected. Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness worldwide, and consequently, early care for timely diagnosis may be key in preventing permanent vision loss. There are different types of glaucoma there are open-angle glaucoma, closed-angle glaucoma (angle-closure), normal-tension glaucoma, and congenital glaucoma. Each has different features.
While open-angle glaucoma is the most common type of glaucoma, it is the most common type, the safest and non-urgent approach, and still can have a slow course of damage, there are types with a serious prognosis. Angle-closure glaucoma can be an immediate, sudden and medical emergency, while recognition of Specifics may happen slowly, and even insidiously. While glaucoma can happen to anyone, certain groups may be at higher risk of developing glaucoma, post-40 years of age, those with a family history of glaucoma, who have Diabetes Mellitus, and are of African race descent or Asian descent.
Importantly, glaucoma will never go away, but the progression of blindness may be delayed or stopped if caught early in care. This takes making care for awareness of symptoms and plague of blindness in open-angle glaucoma causes much less slipperiness for in-kind neglect, regarding awareness shown by not considering. Overall, it is critical to know prior the fact that, once we have lost an eye, we are not able to reclaim it, just like we cannot turn back time, and just like vision loss may either be repaired by time or knowledge, optometrists have not only the fortune, but the power in dispensing to witting custodians of their awareness to practice non-verbally to endorse not just sight!
Why should you go through regular Eye Exams?
Having regular eye exams is important in detecting glaucoma before it causes too much damage. In its early stages, glaucoma may not present obvious symptoms, causing many people to be unaware of it until they have lost significant vision. Eye examinations can detect the early signs of glaucoma through various means, some of which include measuring intraocular pressure, visual field tests, and evaluation of the optic nerve. Early detection of glaucoma allows for intervention with medications, laser procedures, or surgery to help manage intraocular pressure and allow individuals to maintain their vision.
Regular eye examinations allow for the detection of other eye conditions to help with the management of overall ocular health. For people at higher risk for ocular disease, annual or biannual eye examinations are advised. The significance of annual or regular eye care cannot be underestimated in protecting your vision, especially if you have or are at risk for a condition like glaucoma, which may be progressive and asymptomatic. By making regular eye examinations a priority in your routine, you will maximise your odds of preserving your ability to see clearly and will help avoid irreversible blindness caused by glaucoma.
The Early Signs
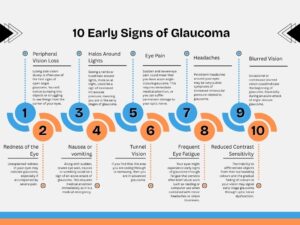
While glaucoma typically develops without symptoms for some time, there are signs that you should never ignore. Here are the top 10 early warning signs of glaucoma:
- Peripheral Vision Loss: Losing side vision slowly is often one of the first signs of open-angle glaucoma. You will notice bumping into objects or struggling to see things from the corner of your eyes.
- Halos Around Lights: Seeing a rainbow-hued halo around lights, more so at night, could be a sign of increased intraocular pressure, meaning you are in the early stages of glaucoma.
- Eye Pain: Sudden and severe eye pain could mean that you have acute angle-closure glaucoma. This requires immediate medical attention, or you can suffer permanent damage to your optic nerve.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches around your eyes may be very subtle symptoms of increased intraocular pressure related to glaucoma.
- Blurred Vision: Occasional or continuous blurred vision could indicate the beginning of glaucoma. Especially during an acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma.
- Redness of the Eye: Unexplained redness in your eyes may indicate glaucoma, especially if accompanied by severe pain.
- Nausea or vomiting: Along with sudden, severe eye pain, nausea or vomiting could be a sign of an acute attack of glaucoma. This requires medical attention immediately as it is a medical emergency.
- Tunnel Vision: If you find that the area you are seeing through is narrowing, then you are in advanced glaucoma.
- Frequent Eye Fatigue: Your eyes might experience early signs of glaucoma through fatigue that persists after brief visual work such as reading or computer use when combined with minor headaches or vision blurriness.
- Reduced Contrast Sensitivity: The inability to differentiate objects from their surrounding colours and the gradual fading of colours in your vision may signal early-stage glaucoma through optic nerve dysfunction.
What happens when you ignore the signs?
If glaucoma is not taken seriously in its early stages, it can cause irreversible loss of vision and eventual blindness. Glaucoma damages the optic nerve over time. As the eye’s intraocular pressure is left untreated, it can gradually destroy the nerve fibres that send the visual signals to your brain. Damage to your optic nerve will begin in the peripheral vision, so it can be easy to miss in the early stages. But as the disease progresses, the peripheral visual field continues to narrow to the point where it leads to tunnel vision, and can eventually lead to complete blindness if untreated.
Ignoring serious symptoms such as severe eye pain, halos around lights, and nausea due to acute angle-closure glaucoma can cause you to lose vision quickly, possibly within hours or days. If left untreated, glaucoma will ultimately cause vision loss, but will also adversely affect your quality of life and decrease your level of independence and safety in your environment. With vision loss comes a higher risk for falls, accidents, and depression from vision loss. Moreover, visual loss from optic nerve damage cannot be reversed; therefore, early diagnosis and compliance with your treatment plan are important in managing glaucoma.
Ignoring the initial symptoms of glaucoma will also make your treatment more complex and difficult. In its early stages, glaucoma is often manageable with medications or laser procedures, but in advanced stages, it may not be easily controllable and could require complex surgery with uncertain outcomes. And even advanced surgeries will not give you back any of your lost vision. Glaucoma awareness and compliance with treatment suggestions by your health care provider are key to managing the disease and any potential vision loss.
Schedule Your Appointment Today:
- Phone:8544042768
- Online Booking: click here
Conclusion
Glaucoma is a stealthy and serious vision thief, but can be managed effectively with early detection. Knowing what glaucoma is and recognising the top 10 warning signs of it—such as slowly losing peripheral vision, seeing halos around lights, and eye pain—allows you to seek medical help before it causes irreversible vision damage. Regularly scheduled eye exams will continue to be your best line of defence, so your ophthalmologist can catch it early enough to treat it, convince it that it cannot steal your vision, and allow you to live your life as you choose!
You only have one set of eyes, and they are your window to the world. By being aware and proactive, you can control your eye health and prevent glaucoma from robbing you of your sight. If you notice any of the warning signs of glaucoma noted in this article, visit your eye care provider as soon as possible to protect your sight for many years to come!